Cyanomethanimine is a chemical intermediate in the proposed synthetic routes of adenine, which is one of nucleobases of DNA and RNA, and may play an important role in forming biological molecules in the interstellar medium. Cyanomethanimine is one of the products of the photoreactivity of aminoacetonitrile (NH2CH2CN, AAN). AAN can form the smallest amino acid glycine via a Strecker synthesis, while amino acids are the building blocks of peptide bonds and proteins in biological tissues.
Recently, astrochemical group researchers at Xinjiang Astronomical Observation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences built the reaction network of cyanomethanimine and its isomers through theoretical chemistry research, and simulated the complicated and heterogeneous physical environment in and in front of Sgr B2(N) via cold isothermal core, hot core, and C-type shock models using gas-grain code Nautilus. The researchers identified the major formation and destruction routes of cyanomethanimine, and found that the calculated abundances of the cyanomethanimine isomers and the ratio of Z-isomer to E-isomer are both in reasonable agreement with observations for selected environments. In particular, they concluded that these isomers are most likely formed within or near the hot core without the impact of shocks, or in the cold regions with shocks.
The research has been published in Month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. The study sheds new light on the evolution of prebiotic molecules in the harsh interstellar environment.
Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/staa1979
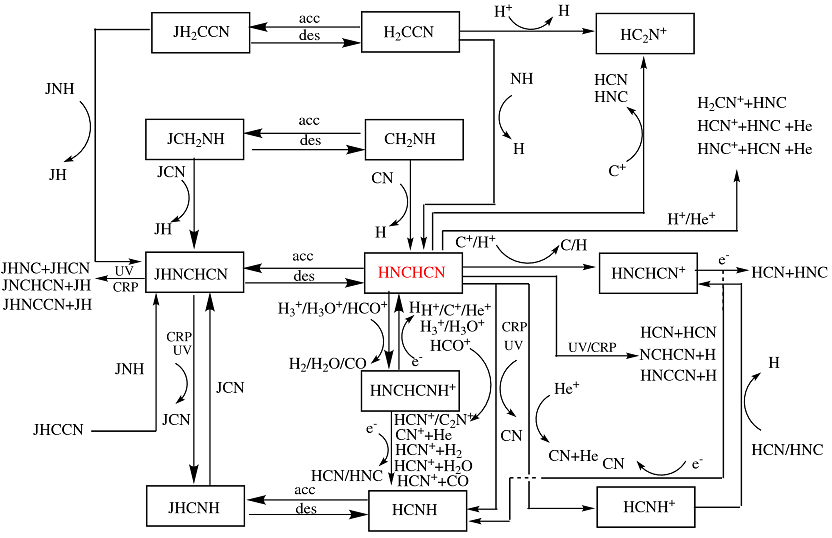
Figure 1. Gas-phase and surface reactions of cyanomethanimine and related species. The E-isomer is shown as an example, the Z-cyanomethanimine and
N-cyanomethanimine isomers have similar reactions.
Contact: ZHANG Xia
Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: zhangx@xao.ac.cn