Recently, an international research team led by Dr. CUI Lang from the Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences, successfully imaged the compact weak radio emission region and measured the astrometric parameters with high precision for the radio star AR Scorpii (AR Sco), by using multi-epoch VLBI observations.
The results were published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS).
VLBI astrometric observations of radio stars can validate the quality of Gaia Celestial Reference Frame (GCRF) and help to improve the accuracy and robustness of the link between the International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF) and GCRF.
AR Sco is the only-known radio-pulsing white dwarf binary to date, consisting of a rapidly rotating magnetic white dwarf and a M-type main-sequence star. It has a broadband spectrum and unusual pulsations detected at the radio, infrared, optical, and ultraviolet bands.
To determine the astrometric parameters of AR Sco at radio band independently, the researchers conducted multi-epoch VLBI phase-referencing observations with the European VLBI Network (EVN) and the Chinese VLBI Network (CVN) plus the New Zealand Warkworth 30-m telescope. Besides the primary calibrator, an additional weak extragalactic source very close to the target AR Sco, played a key role as a secondary calibrator for phase-referencing to improve the astrometric precision when data reduction.
“We detected the compact radio emission (Figure. 1) and provided high-precision astrometric measurements (Figure. 2) for AR Sco. This work provides new and independent astrometric results to validate the Gaia results for AR Sco.” said Dr. Cui.
Based on the astrometric results, they analyzed the kinematics of AR Sco and found that the Galactic space velocities of AR Sco are quite consistent with that of both intermediate polars (IPs) and polars.
Furthermore, the researchers estimated the upper limit of the radio-emitting region size of AR Sco and suggested that the radio emission should be located within the light cylinder of its white dwarf.”
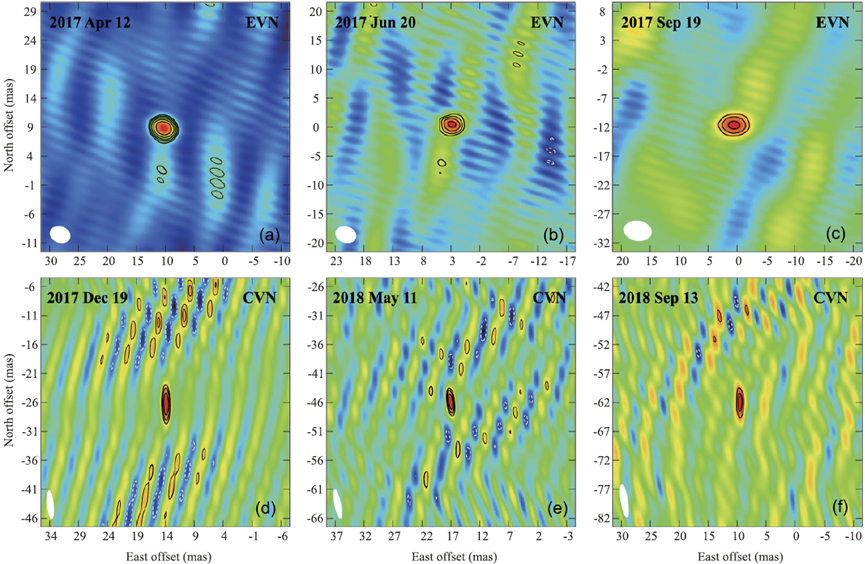
Figure 1. The VLBI images of the WD pulsar AR Sco.
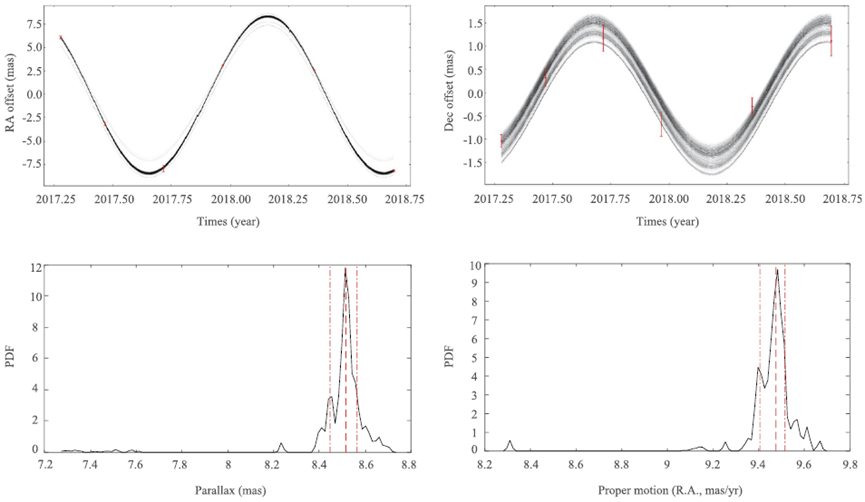
Figure 2. Illustration of the bootstrap astrometric fit for AR Sco.
Contact: JIANG Pengfei; CUI Lang
Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences
E-mail: jiangpengfei@xao.ac.cn; cuilang@xao.ac.cn
Article Link: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2023MNRAS.520.2942J