Using Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) observations, researchers from the Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory (XAO) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have imaged the compact radio emission region and detected radio flare events for a Magnetic Propeller Cataclysmic Variable (MPCV) called LAMOST J024048.51+195226.9 (J0240+1952).
The study was published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters.
MPCVs are a special type of accreting binary that comprises of a fast-rotating magnetic white dwarf and a main sequence companion star. The rapidly rotating magnetosphere of the white dwarf throws out the material accreted from the companion star via a 'magnetic propeller' mode. Compared with the conventional cataclysmic variable (CV) , MPCV has a higher radio luminosity with rapid flux variations. Studying the radio emission of these special sources can help us to explore the radio radiation origin and mechanism, as well as understand the accretion process.
J0240+1952 is a newly discovered MPCV possessing the fastest known rotating white dwarf. The researchers conducted phase-referencing VLBI observations for this source. The phase-referencing technique utilizes a nearby calibrator to perform phase corrections of the target data, hence allowing imaging much weaker sources. By using this technique, the researchers obtained the first view of the radio morphology of J0240+1952 on the milliarcsecond scale and derived the radio light curve of this source.
The compact nature of the radio emission of J0240+1952 was revealed on the astronomical unit (AU) scale, with a brightness temperature of >2.3×10^7 K, confirming a non-thermal origin. Additionally, irregular flux variations of the radio emission were observed on a time-scale of tens of minutes, accompanied by overlapping flare events captured in the second half of the VLBI observation.
Based on these observing features, the researchers suggested that the radio emission of J0240+1952 conforms to the 'magnetospheric-propeller-driven' radiation mechanism. Moreover, the overlapping flare events can be explained by a superposition of synchrotron radiation arising from expanding magnetized blobs of this system.
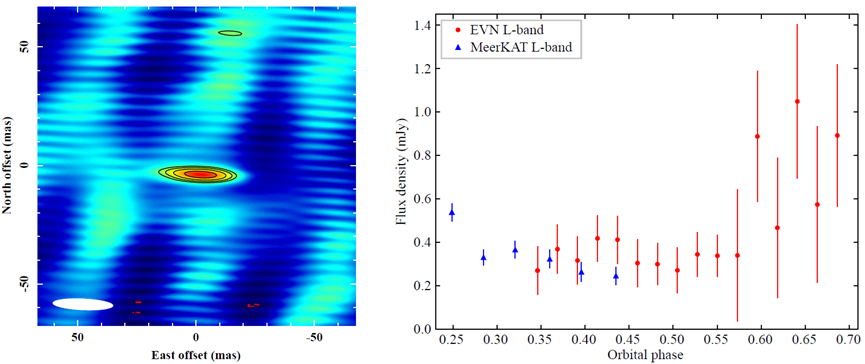
VLBI image (left) and radio light curve (right) of J0240+1952.
Contact: JIANG Pengfei
Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences
E-mail: jiangpengfei@xao.ac.cn
Article Link:https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2024MNRAS.528L.112J/abstract