

New Study Confirms Excellent Astronomical Potential of Muztagh Observation Station
Recently, GU Wenbo, a PhD candidate from the Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with his supervisor Prof. Ali Esamdin and colleagues, conducted a systematic analysis of the seeing and meteorological data. The data, collected from 2018 to 2024 at the Muztagh Station’s North-1 and North-2 points, revealed the site's unique advantages for optical observations. The research findings have been published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
As starlight travels through Earth’s atmosphere, it is affected by atmospheric optical turbulence; the resulting refractive-index fluctuations distort the optical wavefront and degrade a telescope’s imaging quality. Seeing reflects the degree of blurring and positional jitter of stellar images caused by atmospheric optical turbulence and is one of the core indicators for evaluating the quality of an observatory site. This study utilized a Differential Image Motion Monitor (DIMM), a 30-meter meteorological tower, and a PC-4A automatic weather system to acquire key parameters for the Muztagh Observatory, including seeing, temperature, wind speed, and wind direction.
The monitoring results show that the seeing conditions at the Muztagh Station are excellent. The median seeing at the North-2 point at a height of 10 meters is 0.78 arcseconds, and at the North-1 point at a height of 6 meters, it is 0.89 arcseconds. Simultaneously, the site has a small nighttime ground-surface temperature difference (about 2°C), moderate wind speed (median value of 5–6 m/s), and a stable, dominant wind direction (southwest).
The study also conducted an in-depth exploration of the impact of dynamic wind fields on seeing. The research found a significant "U-shaped" relationship between seeing and wind speed, where moderate wind speeds are most favorable for suppressing atmospheric turbulence and optimizing seeing. Airflow from the dominant wind direction usually brings better seeing, whereas strong vertical wind shear and short-term, drastic fluctuations in wind speed will significantly enhance atmospheric turbulence, leading to a deterioration in seeing.
With its excellent near-ground turbulence environment and seeing conditions, the Muztagh Station shows great potential to become an outstanding optical astronomical observatory site in Western China. This research was funded by a project from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
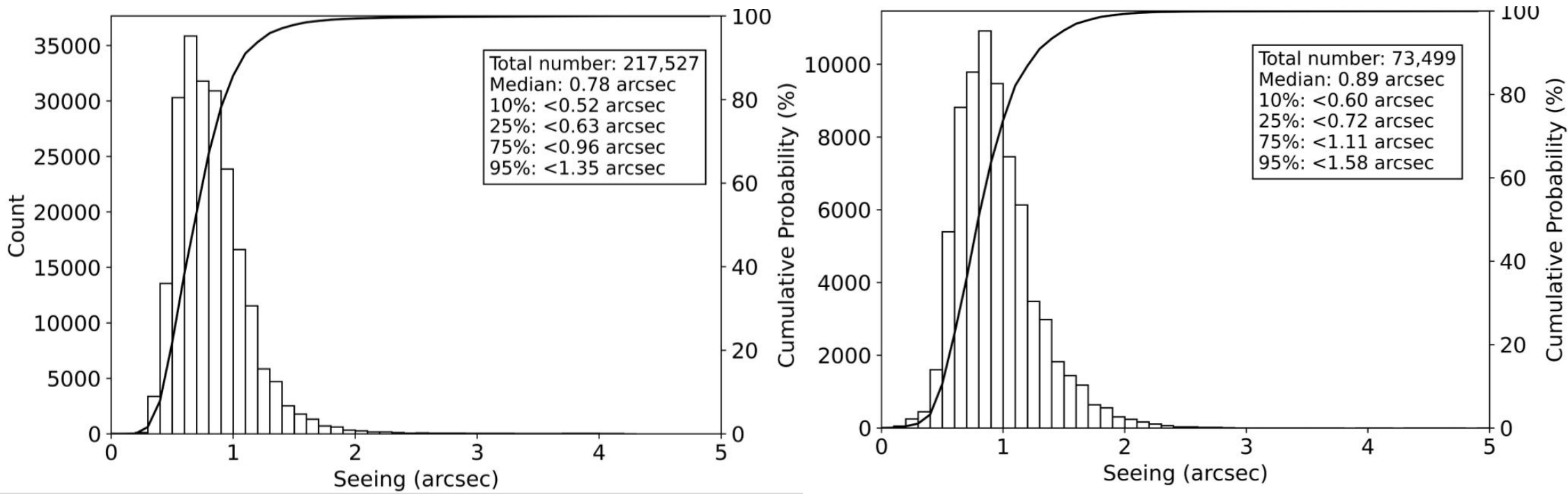
Left: Seeing Statistics Chart at 6m Height - North Point 1, Muztagh-Ata Observatory; Right: Seeing Statistics Chart at 10m Height - North Point 2, Muztagh-Ata Observatory
Attachment Download: