OJ 287 is a typical blazar with relativistic jets, and because the jet point very close to the observer's line of sight, they show a strong beaming effect. At present, flares of about 12 years period have been observed in the optical band, and observations in the radio band seem to have evidence too. A type of dual black-hole model believes that the secondary black hole passing through the accretion disk of the primary one causes its periodic flare; the other type of model believes that it comes from the relativistic beaming effect of the jet, and the jet precession produces the periodic flare. Therefore, how to distinguish these two models is a frontier topic for further understanding the evolution of active galactic nuclei.
YUAN Qi, a doctoral student from the Galaxy cosmology research group of Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, under the guidance of Prof. LIU Xiang and Prof. ZHANG Ming, analyzed the cross-correlation between jet observables by using the multi-band and multi-epoch VLBI monitoring data of the blazar OJ 287. It was successfully verified that the co-modulation properties among the observables could be attributed to the geometric effect of jet precession.
Relevant research results have been officially published in the American "Astrophysical Journal" (ApJ, 2023, 949 (1):20).
By mapping and model-fitting the radio interferometry data, the researchers extracted the core flow density, the position angles of the inner and outer jets, and the polarization position angle of the core. Then the Monte Carlo method is used to sample and consider the prior influence of the observable errors. The cross-correlation analysis between observables was carried out, and the correlation results with a significance level of 95% were obtained (as shown in the Figure). The correlation between the core flux density and the position angles of the inner and outer jet is detected, and this can be explained by the precession model.
This study showed that the precessing candidates of active galactic nucleus can be selected by using the correlation analysis method, without complex parameterized model fitting to jet kinematics. In addition, the researchers did not find any strong correlation between the polarization position angle of the core and the internal jet position angle at 15 GHz and 43 GHz, implying that the order of the polarization position angle in the core region at those frequency bands is low.
The correlations between observations found in OJ 287 are not an accidental property of that particular data set. In the next step, the researchers will conduct multi-sample statistical analysis on AGNs with similar characteristics. The derived observations of correlation can thus be used to classify AGN samples and further explore the applicability of the unified model, which will have far-reaching implications on the blazars research.
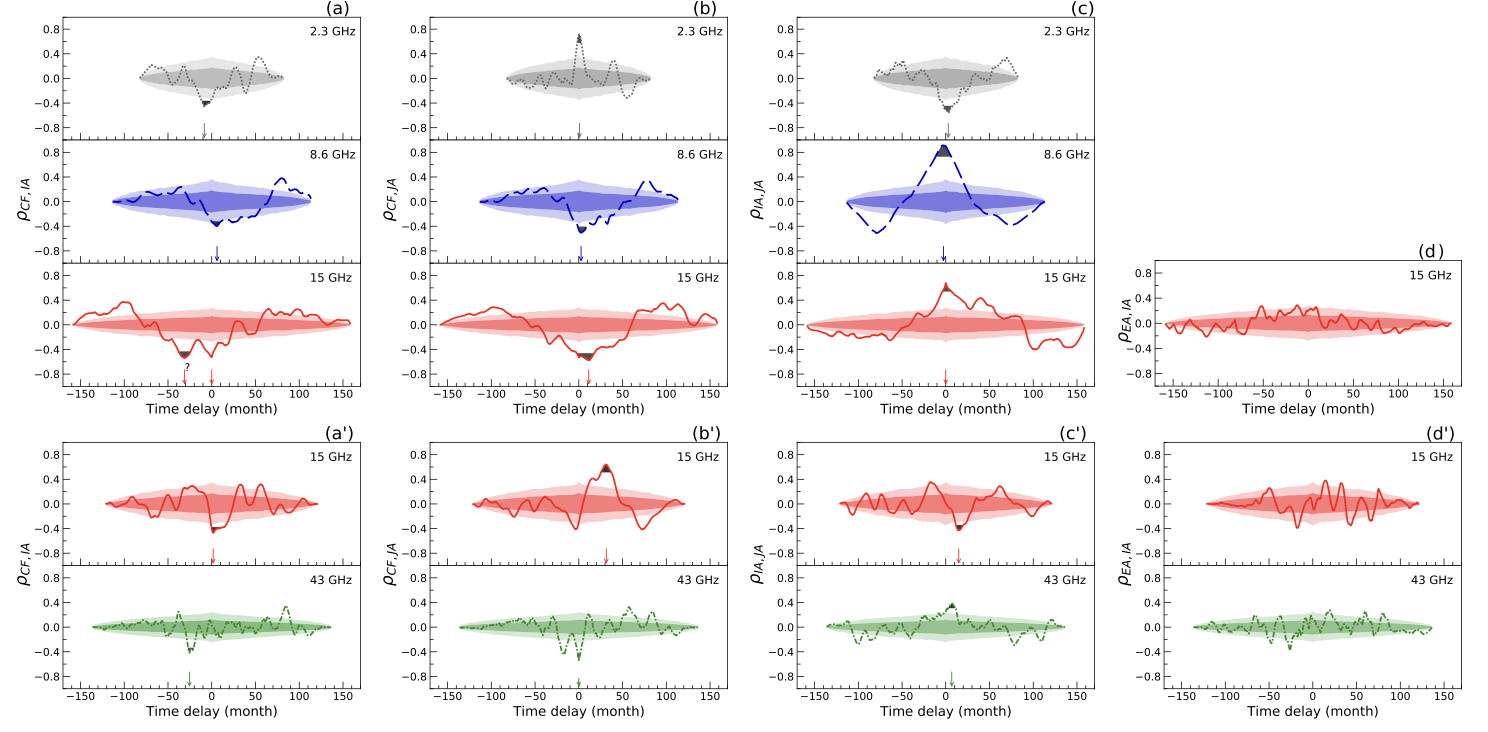
Figure. Results of correlation test between different observables
Contact: YUAN Qi; ZHANG Ming
Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: yuanqi@xao.ac.cn zhangm@xao.ac.cn
Article link:https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4357/acc5ec/pdf