

Research progress of the formaldehyde absorption line in Molecular Clouds
The distribution of H2CO absorption in the Galaxy and against 262 Galactic radio sources has been surveyed showing that H2CO absorption is associated with most of the H II regions. Since H2CO is only seen in absorption against a background continuum it only samples the physical conditions in the foreground of the H II region, while other millimeter and submillimeter spectral lines are observed both in front and behind the source.
Toktarkhan Komesh from Kazakhstan (CAS-TWAS President's Fellowship winner), a PhD student of the star formation and evolution group at XAO, determined the excitation temperature of the H2CO absorption in the molecular cloud. He proved that the sensitive mapping of H2CO absorption has been able to correctly identify star formation activity in complex molecular clouds such as the Aquila Complex. In addition, the detailed structure of the absorption lines may reveal discrepant velocity components resulting from outflow regions.
The related work has recently been published in The Astrophysical Journal (ApJ,2019,874,172)
The link to the full paper: http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2019ApJ...874..172K
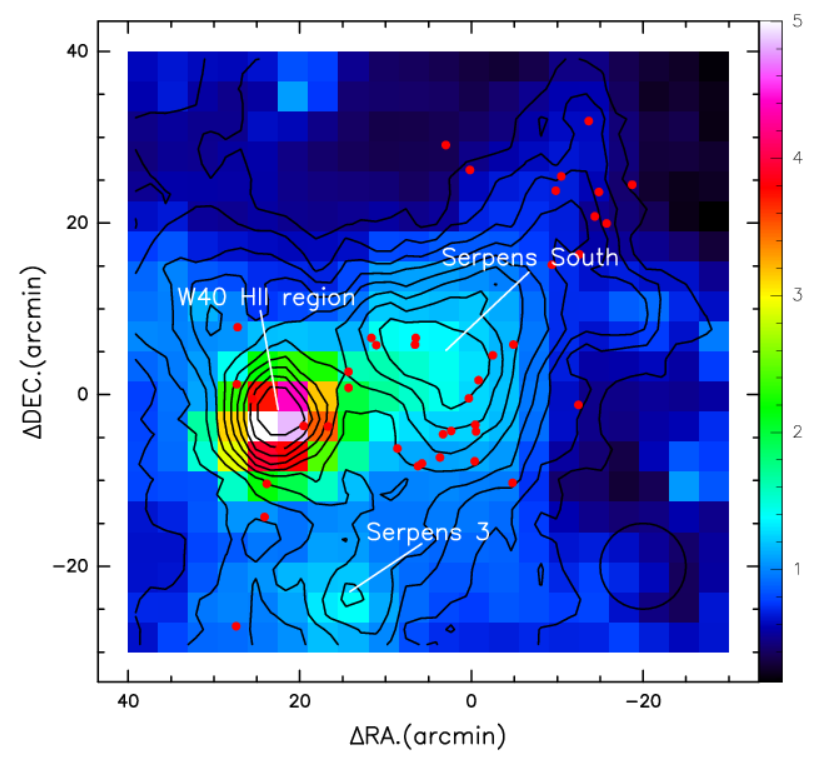
Distribution of Tex of H2CO absorption line superposed on the integrated absorption contours of H2CO
Attachment Download: